 Vancouver Vancouver
 
(L) Aerial view of the University of British Columbia campus (R) The entrance
of UBC Hospital
  
The sign board of the University of British Columbia Hospital
The buildings and grounds are smoke-free.
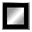
The main entrance, corridor and the exterior of UBC Hspital
The UBC Hospital, located on the University Endowment Lands next to Vancouver,
opened in 1968. The
Units include; the Acute Care Unit, Surgical Observation Unit and Urgent
Care Centre, the Extended Care
Unit and Transitional Care Unit, and the Psychiatric Unit. UBC Hospital has eight operating rooms and 800
staff, including 270 physicians and 450 nurses. There areapproximately 28,000 clinic visits to the hospital.
  
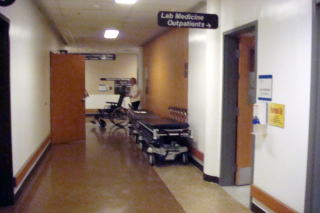
St.Paul's Hospital, on the Burrard Street, downtown, Vancouver
 
The entrance and reception lobby of St.Paul's Hospital
The corridor of St.Paul's Hospital
  
(L) The hospital buildings and grounds are smoke-free.
(M) A management of St.Paul's Hospital is carried out, similar to other
hospitals, with a financial assistance of donation.
(R) A medical office building for a practicing physician, at the downtown
Vancouver
St. Paul's Hospital is an acute care, teaching, in affiliation with the
University of British Columbia Faculty
of Medicine, and research hospital located in downtown Vancouver. It is the largest of the seven health
care facilities operated by Providence Health Care, a Roman Catholic faith-based
care provider.
  
(L) A notice in order to exclude a drug addict, observed in Squamish, British
Columbia.
(R) OxyContin ( Oxycodone ) is an opioid analgesic drug, which is generally
prescribed for the relief of severe pain.
This sign plate was found in the town of Jasper.

Dental office at Metrotown, Vancouver
 
The inside of the dental office is quite open.
 Calgary Calgary
Alberta Health Services is the provincial health authority responsible
for planning and delivering health
supports and services for more than 3.7 million adults and children living
in Alberta. Its mission is to
provide a patient-focused, quality health system that is accessible and
sustainable for all Albertans.
The new McCaig Tower at the Foothills Medical Centre in Calgary is the result of a 10-year vision to expand
the Foothills Campus, based on the needs of the population of Calgary and
surrounding area. It will
incorporate existing services at the Foothills Hospital, but the modern
design, proximity and efficiency,
will allow for improved delivery of those services. By relocating some of the existing services at the
Foothills into the new building, space will also be created to expand other
areas of the hospital, including
the emergency department.
Among other services, the McCaig Tower will include:
- Seven operating rooms and a new interventional trauma operating room, which is the first for its kind
- in Canada.
- A new 36-bed ICU unit which will incorporate the existing 25-bed ICU.
- Improvements in infection prevention and control
This new addition will include 93 inpatient beds, 36 bed intensive care
unit, 21 short-stay beds, a total
of 150 additional beds, as well as eight operating rooms.
Reference: Wikipedia
 
(L) McCaig Tower (R) University of Calgary Foothills Campus
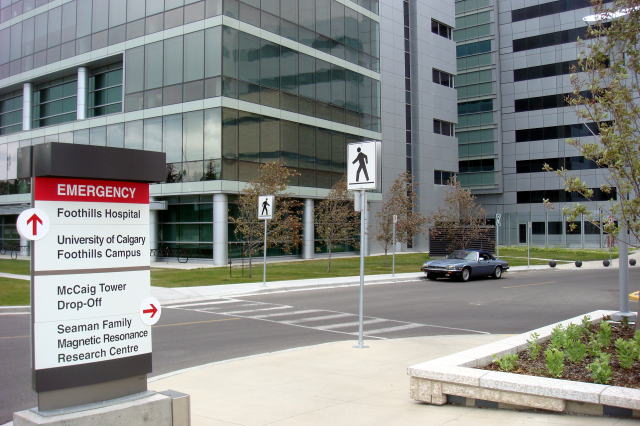
 
A sign board of McCaig Tower and Alberta Health Services
  
A waiting room with a fireplace of the new hospital building and corridor
  
(L) One of the entrance to the new hospital (M) Access information panel
(R) The entrance to the diagnostic Imaging room
 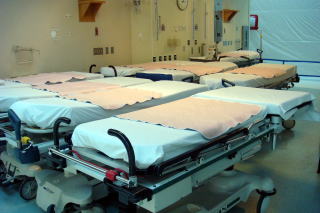 
(L) An information board of the new building (R) A strecher and emergency
ward
 
(L) A corridor of a new hospital to the main building, Foothills Medical
Centre
(R) All medical facilities are smoke-free.
Foothills Medical Centre (FMC) is the largest hospital in Alberta. It is one of Canada's mostrecognized
medical facilities and is one of the leading hospitals, providing advanced
healthcare services to over
two million people from Calgary, Southern Alberta, southeastern British
Columbia, and southern
Saskatchewan.
  
(L) The main entrance to the Foothills Hospital, University of Alberta
(M) Hospital cafeteria (R) A corridor of the main building
 
Hospital power plant
The Foothills hospital site receives about 50 percent of its power supply
from two steam turbine generators
located on the site. The oil coolers on the generators use river water
for cooling via a heat exchanger where
the oil and water do not normally come into contact. A booster pump assists with water circulation. The
water discharge is normally returned back to the Bow River through the
storm water system. Its power
plant was first built in 1968. The electricity production of this plant
was 22,507 MWh in 2007.
 
(L) Health Sciences/Jubilee train station (R) Buildings in the University
Hospital complex at the University of Alberta
 Edmonton Edmonton
The University of Alberta Hospital (UAH ) is a research and teaching hospital
in Edmonton. The hospital is
affiliated with the University of Alberta and run by Alberta Health Services, It has a total of 650 beds and
treats over 700,000 patients annually. The whole hospital complex is served
by the Health Sciences/Jubilee
light rail transit station.
 
Walter C. Mackenzie Health Science Centre
 
(L) No smoking is always mandatory in the medical facilities. (R) Stollery
Children's Hospital
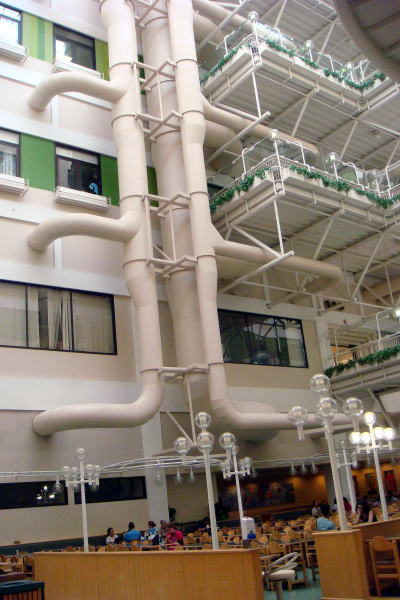
 
An own piping systems as an art, seen in the hall of Walter C. Mackenzie
Health Science Centre
  
(L) Gift shop un the piping systems of the hospital (M) Directory of various
sections
(R) No smoking sign, saying for maintaing clean and healthy environment
 
(L) Smoking is not permitepermited nearnearthe hspital entrance (R) Edmonton
Clinic, University of Alberta
The Edmonton Clinic North is scheduled d for completion in 2011, and the Edmonton Clinic South in 2012.
The joint venturebetween the University of Alberta and Alberta Health Services
is funded by the Province
of Alberta. The facility will be housed in two separate buildings, with
the north building, known as the
Edmonton Clinic Health Academy, focused on research and teaching, and the south building specializing
in clinical aspects.
 
(L) National Institute for Nanotechnology, University of Alberta
(R) The Centre for Pharmacyand Health Research, North Campus of the University
of Alberta
National Institute for Nanotechnology, ( NINT ), Canada's flagship nanotechnology
institute, aims to establish
Alberta as a leading centre of innovation and commercial enterprise in the field of nanotechnology. Its funding
comes from the Government of Canada, the Government of Alberta, and the
University of Alberta. The 200,000
square metre NINT building is one of the most technologically advanced
research facilities in the world and
houses the characterization suite, which is one of the quietest laboratory spaces in Canada. The building was
officially opened in 2006.
カナダの医療制度は日本と異なり、予約のいらない「ウォーク・イン・クリニック」、患者がかかりつけの医師を決め、
予め登録の必要な「ファミリードクター」、その上に「専門医」とがある。「ウォーク・イン・クリニック」では2時間
程度の待ち時間は覚悟しておかねばならないが、ネット上で待ち時間を公開しているようである。他はすべて予約制と
なっているので待ち時間はほとんどない。「専門医」を直接受診することは出来ず、先ず「ファミリードクター」の
診察、紹介が必要となる。
大都市の病院では高度の医療がほどこされ、辺地診療には大学病院からヘリコプターも使用され、定期的に医師が
派遣されている。地域の保健機構に登録さえしておれば医療費は歯科診療を除いてすべて無料である。ただし薬代は
有料となっている。この原則は筆者がカナダで診療していた1970年代当時と同じである。
今回の病院視察で、古い施設をそのまま利用しているところと、カルガリーのように、最新鋭の医療設備で高度の診療
を行っているところがあった。病院内は患者さんおよび面会者に広く解放されており、病院スタッフはとても親切である。
驚くべきことは、カルガリー大学病院には二つのタービンエンジンを使用、ボウ川の水を利用した大規模な自家発電
装置があり、病院に必要な電力の50%を供給していることである。アルバータ州の一人当たりのGDPは75,000ドルと
カナダ平均の46,440ドルを大きく引き離しており(2007年)、こうした背景もカルガリーなどの都市部で見られる
高度医療施設の建設を後押ししているのかもしれない。
  Smoking ban in British Columbia and Alberta, Canada Smoking ban in British Columbia and Alberta, Canada
 London Health Sciences Centre, Ontario London Health Sciences Centre, Ontario
 UCSF Medical Center 2012 UCSF Medical Center 2012
Canada
 British Columbia British Columbia  Alberta Alberta  Trip to Canada 2011 Trip to Canada 2011  Vancouver Vancouver  North Vancouver North Vancouver  Whistler Whistler
 Skytrain Skytrain  VIA train VIA train  Jasper Jasper  Icefield and Bow Summit Icefield and Bow Summit  Emerald Lake Emerald Lake  Lake Louise Lake Louise  Banff Banff  Calgary Calgary
 Edmonton Edmonton  Hospitals in BC and Alberta Hospitals in BC and Alberta  Tobacco control in B.C. and Alberta 2011 Tobacco control in B.C. and Alberta 2011
 カナダ BC, アルバータの病院 カナダ BC, アルバータの病院
 2011年7月執筆 医学博士 宮本順伯 2011年7月執筆 医学博士 宮本順伯
★This Web site is link-free.
This information was provided by the Smokefree Hotel and Travel.
The article was written and photographs were taken by Junhaku Miyamoto, M.D.,PhD., in July 2011.
Copyright (C) 2011 Junhaku Miyamoto, PhD. All right is reserved.
|
